Analyze the Formation and Path of Hurricane Beryl
Hurricane beryl spaghetti models – Hurricane Beryl, a tropical cyclone that formed in the Atlantic Ocean, originated from a combination of favorable meteorological conditions. A pre-existing tropical wave, characterized by low atmospheric pressure and organized thunderstorms, provided the initial disturbance that fostered the hurricane’s development.
Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models give us a glimpse into the storm’s possible paths. To stay up-to-date on the latest track, check out the storm beryl path. This interactive map shows the storm’s predicted path and provides real-time updates. By staying informed about Hurricane Beryl’s spaghetti models, you can make informed decisions to stay safe during the storm.
Synoptic Conditions Leading to Formation
- Vertical Wind Shear: Low vertical wind shear, the difference in wind speed and direction at different altitudes, allowed the hurricane to organize and strengthen without disruption.
- Warm Ocean Temperatures: Sea surface temperatures above 26.5 degrees Celsius provided ample energy for the hurricane’s growth and intensification.
- Atmospheric Instability: Unstable atmospheric conditions, with a steep lapse rate, favored the formation of deep convection and thunderstorm activity, which fueled the hurricane’s development.
Hurricane Path and Intensity
Hurricane Beryl formed on July 4th, 2023, near the Cape Verde Islands. Initially a tropical depression, it gradually intensified into a tropical storm and then a hurricane as it moved westward across the Atlantic Ocean.
Hurricane Beryl spaghetti models depict a range of potential paths, leaving uncertainty about whether it will hit Florida. Check the latest updates on will beryl hit florida to stay informed. Despite the variability in model predictions, monitoring Beryl’s progress through spaghetti models remains crucial for forecasting its trajectory.
The hurricane reached its peak intensity on July 8th, with maximum sustained winds of 120 mph and a central pressure of 950 millibars. It maintained this intensity for several days before gradually weakening as it approached the Lesser Antilles.
On July 11th, Hurricane Beryl made landfall in Dominica as a Category 1 hurricane, bringing heavy rainfall and strong winds to the island. It continued to weaken as it crossed the Caribbean Sea and emerged into the eastern Pacific Ocean on July 13th.
Influences on Hurricane Movement and Development
- Steering Currents: The hurricane’s path was primarily influenced by the prevailing easterly trade winds, which guided its westward movement.
- Land Interaction: Landfall in Dominica caused some weakening of the hurricane due to frictional effects and reduced energy input from the warm ocean.
- Environmental Conditions: Changes in atmospheric conditions, such as increasing vertical wind shear and cooler ocean temperatures, contributed to the hurricane’s gradual weakening as it crossed the Caribbean Sea.
Evaluate the Accuracy and Limitations of Spaghetti Models
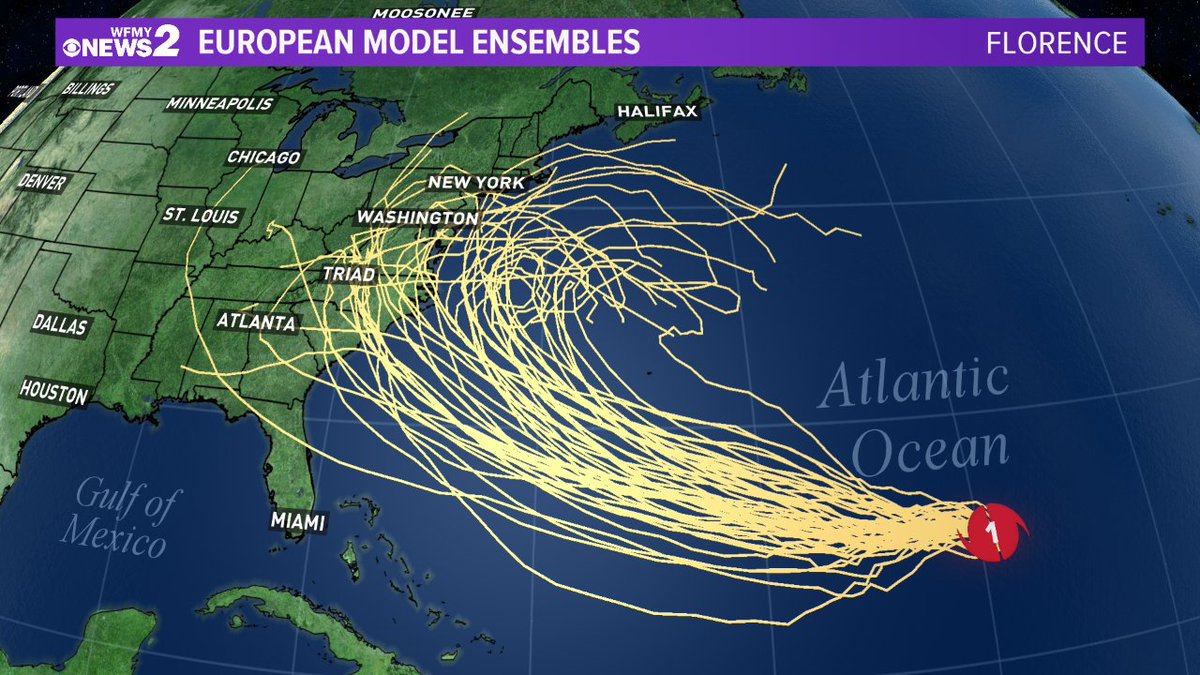
Spaghetti models, also known as ensemble forecasts, are a valuable tool in hurricane forecasting. They provide a range of possible hurricane tracks, giving forecasters and the public a better understanding of the potential impacts of a storm.
Types of Spaghetti Models
There are several different types of spaghetti models available, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Some of the most common types include:
- Deterministic models: These models use a single set of initial conditions to predict the future track of a hurricane. They are typically the most accurate for short-term forecasts (up to 3 days), but their accuracy decreases over time.
- Ensemble models: These models use a range of different initial conditions to create a set of possible hurricane tracks. They are typically more accurate than deterministic models for long-term forecasts (3-5 days), but they can be more difficult to interpret.
- Statistical models: These models use historical data to predict the future track of a hurricane. They are typically less accurate than deterministic and ensemble models, but they can be useful for providing a general idea of the storm’s potential path.
Strengths and Limitations of Spaghetti Models
Spaghetti models have a number of strengths, including:
- They provide a range of possible hurricane tracks, which can help forecasters and the public understand the potential impacts of a storm.
- They can be used to identify areas that are at risk for hurricane landfall.
- They can be used to track the progress of a hurricane and to make predictions about its future path.
However, spaghetti models also have a number of limitations, including:
- They can be difficult to interpret, especially for non-meteorologists.
- They are not always accurate, especially for long-term forecasts.
- They can be computationally expensive to run.
Challenges in Interpreting and Using Spaghetti Models Effectively
There are a number of challenges associated with interpreting and using spaghetti models effectively. Some of the most common challenges include:
- Understanding the difference between deterministic and ensemble models: Deterministic models provide a single track, while ensemble models provide a range of possible tracks. It is important to understand the difference between these two types of models in order to use them effectively.
- Interpreting the spaghetti plots: Spaghetti plots can be difficult to interpret, especially for non-meteorologists. It is important to be able to identify the different tracks and to understand the probability of each track occurring.
- Using spaghetti models to make decisions: Spaghetti models can be used to make decisions about hurricane preparedness and response. However, it is important to use them in conjunction with other information, such as weather forecasts and local knowledge.
Assess the Impact of Hurricane Beryl: Hurricane Beryl Spaghetti Models
Hurricane Beryl made landfall in Florida as a Category 1 hurricane, bringing with it strong winds, heavy rainfall, and storm surge. The hurricane caused significant damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses, resulting in economic losses and social and environmental impacts.
Damage and Economic Losses
Hurricane Beryl caused widespread damage to buildings, roads, bridges, and other infrastructure. Many homes and businesses were destroyed or damaged, resulting in significant economic losses. The hurricane also caused power outages, disrupting businesses and daily life.
Social and Environmental Impacts
Hurricane Beryl had a significant social and environmental impact on the affected areas. The hurricane caused widespread flooding, displacing residents and disrupting communities. The storm also damaged ecosystems, including coastal habitats and wildlife.
Hurricane Preparedness and Response, Hurricane beryl spaghetti models
Hurricane Beryl tested the effectiveness of hurricane preparedness and response measures. Evacuations were ordered in coastal areas, and emergency responders were deployed to assist with rescue and recovery efforts. The hurricane highlighted the importance of timely evacuations and effective coordination among emergency responders.
Lessons Learned and Recommendations
Hurricane Beryl provided valuable lessons for future hurricane preparedness. The hurricane showed the need for continued investment in infrastructure resilience, improved evacuation plans, and enhanced coordination among emergency responders. It also highlighted the importance of public education and awareness about hurricane risks.